A cyber security management system (CSMS) is a framework for organizing and putting into practice the policies, processes, and technical safeguards that a company uses to safeguard its crucial assets and data against cyber threats. An organization’s cyber security management system (CSMS) typically consists of a set of policies and procedures outlining the roles, responsibilities, and steps involved in managing cyber security. To defend the organization’s networks, systems, and data from cyberattacks, it also consists of technological solutions like firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection and prevention systems.
A CSMS’s objective is to support enterprises in preventing, detecting, and swiftly and effectively responding to cyber threats. It is intended to guarantee that a company’s crucial assets and data are shielded from unwanted access, abuse, or destruction. Employing a CSMS enables firms to lower their vulnerability to cyberattacks and lessen the impact of any assaults that do take place.
What are the 5 types of cyber security? | What are the 3 major types of cyber security?
Organizations can utilise a variety of cyber security techniques to shield their networks, systems, and data against online dangers. These consist of:
- Network security: This entails guarding a company’s systems and networks against illegal access, data breaches, and other online threats. In order to safeguard the network, intrusion detection and prevention systems, firewalls, and other technical measures are frequently used.
- Application security: This entails guarding against weaknesses and attacks on the applications that a company utilizes. To make sure that applications are secure, it comprises steps like input validation, secure coding techniques, and regular security testing.
- Endpoint security: Endpoint security entails safeguarding the PCs, laptops, and mobile devices that are linked to a company’s network. It comprises safeguards against malware and other online threats, including firewalls, antivirus software, and other technical measures.
- Data security: Data security is the process of preventing unwanted access to or misuse of an organization’s data. To ensure that data is secure, it consists of methods like encryption, data backup and recovery, and access limits.
- Identity and access management: Identity and access management is the process of managing and restricting access to the networks, systems, and data of an organization. To ensure that only authorized users may access crucial assets and data, it comprises procedures like user authentication, password rules, and access controls.
Why is cyber security management important?
Organizations can utilize a variety of cyber security techniques to shield their networks, systems, and data against online dangers. These consist of:
- Network security: This entails guarding a company’s systems and networks against illegal access, data breaches, and other online threats. In order to safeguard the network, intrusion detection and prevention systems, firewalls, and other technical measures are frequently used.
- Application security: This entails guarding against weaknesses and attacks on the applications that a company utilizes. To make sure that applications are secure, it comprises steps like input validation, secure coding techniques, and regular security testing.
- Endpoint security: Endpoint security entails safeguarding the PCs, laptops, and mobile devices that are linked to a company’s network. It comprises safeguards against malware and other online threats, including firewalls, antivirus software, and other technical measures.
- Data security: Data security is the process of preventing unwanted access to or misuse of an organization’s data. To ensure that data is secure, it consists of methods like encryption, data backup and recovery, and access limits.
- Identity and access management: Identity and access management is the process of managing and restricting access to the networks, systems, and data of an organization. To ensure that only authorized users may access crucial assets and data, it comprises procedures like user authentication, password rules, and access controls.

Cyber security management course
An educational program that teaches people the concepts and procedures of managing cyber security within an enterprise is known as a cyber security management course. Typical subjects covered in these courses include risk management, incident response, security policy, and technical safeguards like firewalls and antivirus software.
There may be different degrees of cyber security management courses available, from foundational courses that cover the fundamentals to advanced courses that delve into more specific subjects. They may be a part of a degree program or certificate program, and they may be provided online or in a conventional classroom setting.
Courses on cyber security management are primarily intended for professionals in the industry, including IT specialists, network administrators, and security analysts. To learn more about cyber security and how to defend their companies from dangers, professionals in other professions might also find them helpful.
What are the 7 layers of cyber security?
The “7 layers of security” framework is one of the most often used methods for structuring the many components of cyber security. The networks, systems, and data of a business are protected from cyber attacks by this framework’s seven separate levels, each of which has a specialised function.
The following are the seven layers of cyber security:
- Physical security: Physical security entails preventing unauthorized access to and tampering with an organization’s physical assets and infrastructure. It consists of safeguards including locks, fences, and surveillance cameras.
- Network security: This entails guarding a company’s systems and networks against illegal access, data breaches, and other online threats. It contains safeguards for the network’s security such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other technical measures.
- Endpoint security: Endpoint security entails safeguarding the PCs, laptops, and mobile devices that are linked to a company’s network. It comprises safeguards against malware and other online threats, including firewalls, antivirus software, and other technical measures.
- Application security: This entails guarding against weaknesses and attacks on the applications that a company utilizes. To make sure that applications are secure, it comprises steps like input validation, secure coding techniques, and regular security testing.
- Data security: Data security is the process of preventing unwanted access to or misuse of an organization’s data. To ensure that data is secure, it consists of methods like encryption, data backup and recovery, and access limits.
- Identity and access management: Identity and access management is the process of managing and restricting access to the networks, systems, and data of an organization. To ensure that only authorized users may access crucial assets and data, it comprises procedures like user authentication, password rules, and access controls.
- User awareness and training: This entails enlightening users on best practices for cyber security and guiding them in understanding how to defend the assets and data of their organizations from cyber attacks. It covers actions like user education and training, password management training, and security awareness training.
What skills are needed for cyber security?
Those working in the subject of cyber security can benefit from a wide variety of skills. The following key competencies are frequently sought after by cyber security professionals:
- Technical expertise: Cybersecurity professionals should have a strong understanding of computer systems and networks, and be skilled in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities and threats.
- Problem-solving skills: Cybersecurity professionals should be able to identify and solve problems quickly and effectively, particularly in high-pressure situations.
- Communication skills: Cybersecurity professionals should be able to clearly and effectively communicate technical information to non-technical audiences, both in writing and orally.
- Attention to detail: Cybersecurity professionals should be able to pay close attention to details and have a high level of accuracy when working with technical information.
- Time management skills: Cyber security professionals may be required to handle multiple tasks and projects concurrently, and should be able to effectively manage their time and prioritize their work.
- Adaptability: Cybersecurity professionals should be able to adapt to new technologies and changing threats quickly and effectively.
- Teamwork: Cybersecurity professionals often work in teams, and should be able to work effectively with others to achieve common goals.
Depending on their individual duties and responsibilities, cyber security experts may additionally need specialised skills and expertise in addition to these general ones. For instance, a cyber security manager may require excellent leadership and management abilities, but a cyber security analyst may require sophisticated knowledge of computer programming languages.
Can I learn cybersecurity without coding?
Without extensive coding abilities, it is still possible to learn and work in the subject of cyber security, however, some familiarity with coding and programming is helpful.
Developing and putting into practice security policies and processes, administering security tools and systems, and performing security assessments are just a few of the numerous cybersecurity-related tasks that don’t require coding expertise. Although these duties may include the use of security tools and software, in-depth coding expertise is often not necessary.
Cybersecurity analysts, for example, who are in charge of locating and addressing coding vulnerabilities, may need a deeper understanding of coding and programming languages in order to perform their jobs effectively. In certain situations, some familiarity with coding and programming may be advantageous, albeit it is not always necessary for all professions.
Overall, the exact roles and duties of the position will determine the knowledge and abilities needed for a career in cyber security. Coding knowledge is helpful in some situations, but it is not always required for cyber security positions.
Is cyber security easy to study? | Is cyber security difficult?
Studying the area of cyber security can be difficult because it is complex and continuously changing. A solid grasp of computer systems and networks, as well as the numerous risks and vulnerabilities that can influence them, is necessary, as are a variety of technical and non-technical skills and expertise.
The complexity of studying cybersecurity will therefore vary depending on the student’s background knowledge and experience as well as the particular course or program they are enrolled in. Depending on their skills and interests, some people may find learning certain areas of cybersecurity simpler than others.
Breaking the subject of cyber security down into smaller, more manageable pieces and concentrating on one issue at a time are two ways to make it more manageable. To enhance understanding and fill in any knowledge gaps, it can also be beneficial to look for resources like books, online courses, and instructors.
Overall, while studying cybersecurity can be tough, it can also be a rewarding and meaningful field to work in. You can study and achieve in this industry if you put in the effort and persevere.
Is cybersecurity a lot of math?
Most of the time, a high level of math proficiency is not necessary for the subject of cyber security, at least not in terms of complex calculations or mathematical ideas. While some parts of cyber security, like cryptography, may incorporate mathematical concepts, these concepts are often not complex and don’t need highly developed mathematical abilities.
Cyber security experts do, however, need to have a solid understanding of computer systems and networks, which may call for some fundamental familiarity with mathematical ideas like binary numbers and algorithms. Additionally, some positions in the realm of cyber security, such as those of data analysts, may need more complex mathematical abilities in order to evaluate and understand data.
In general, while having a rudimentary understanding of math may be helpful for tasks involving computer systems and networks, it is not often a major need for the majority of cyber security roles.
Can I learn cyber security in 6 months? | Can I learn cyber security in 2 months?
In as little as six or even two months, it is feasible to grasp certain fundamental ideas and abilities linked to cyber security. Although it is unrealistic to expect to become an expert in the subject in such a short amount of time, it is crucial to recognize that the topic of cyber security is broad and complex.
In order to understand cyber security in six or two months, you will probably need to combine self-study with structured learning, such as taking online courses or participating in training sessions. An individual may be able to acquire a fundamental understanding of cyber security ideas and practices in six months or even two months, depending on their specific learning objectives and the amount of time and effort they are able to invest in their studies.
But it’s crucial to remember that mastering cyber security often necessitates a more extensive and continual learning process. It is likely to take considerably longer than six months or two months to really comprehend and master the field.
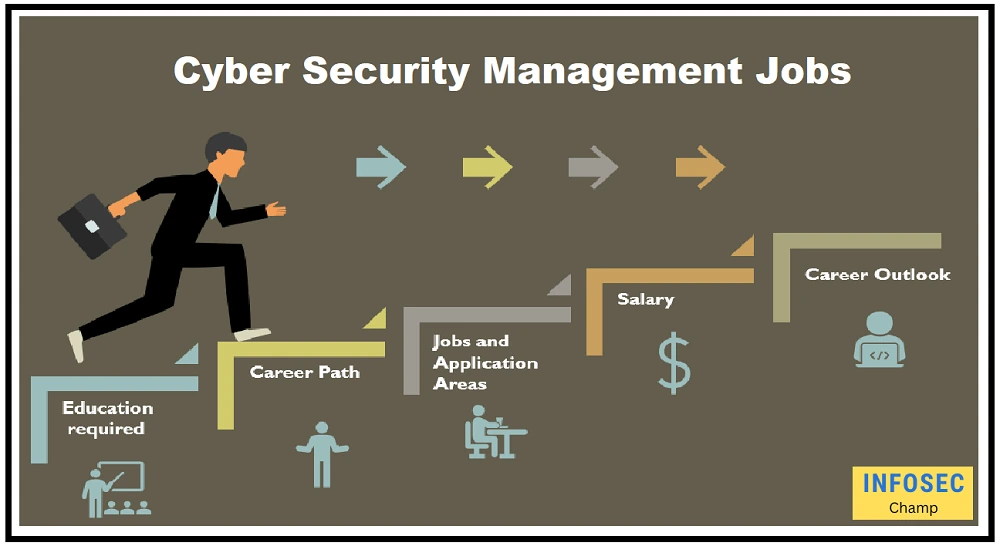
What types of Cyber security management jobs
There are a wide variety of cyber security management jobs available, ranging from entry-level positions to more advanced roles. Some of the types of cyber security management jobs that are commonly available include:
- Cyber security manager: A cyber security manager is responsible for overseeing the overall security of an organization’s networks, systems, and data. They may develop and implement security policies and procedures, manage security tools and systems, and coordinate incident response efforts.
- Cyber security analyst: A cyber security analyst is responsible for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities and threats to an organization’s networks, systems, and data. They may conduct security assessments, monitor for suspicious activity, and analyze security logs and other data to identify potential threats.
- Security engineer: A security engineer is responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining technical security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and antivirus software. They may also be responsible for testing and evaluating new security technologies.
- Security consultant: A security consultant is an expert in cyber security who is hired by organizations to assess their security posture and provide recommendations for improvement. They may conduct security assessments, provide training and education, and develop security plans and policies.
- Information security officer: An information security officer is responsible for ensuring that an organization’s information assets are protected from unauthorized access or misuse. They may develop and implement security policies and procedures, manage security tools and systems, and coordinate incident response efforts.
These are just a few examples of the types of cyber security management (through cyber security training) jobs that are available. The specific job duties and responsibilities of a particular position will depend on the organization and the specific role.
What is Cyber security management salary?
The degree of education, experience, and abilities of the applicant, as well as the precise work duties and responsibilities of the position, will all have an impact on the remuneration for a cyber security management post. Due to the willingness of firms to invest in the knowledge and abilities required to safeguard their networks, systems, and data against cyber attacks, cyber security management positions typically pay well.
The median annual salary for information security analysts, a job category that includes some cyber security management positions, was $99,730 as of May 2020, according to statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). However, depending on the person’s degree of education, experience, and talents, as well as the precise job duties and responsibilities of the position, this number might change dramatically.
For instance, a cyber security manager with advanced training and a proven track record may be paid more than a cyber security analyst with less training and experience. The pay for a cyber security management post may also depend on the particular sector of the employer’s business as well as the location of the role.
Cyber security management syllabus
The course’s unique goals and objectives, as well as its level, will determine the syllabus for a cyber security management course (e.g. undergraduate, graduate, certificate program, etc.). The ideas and procedures for managing cyber security inside an organization will often be covered in a variety of topics in a cyber security management course.
A course on cyber security management might include the following topics:
- Cybersecurity principles and concepts: This may include an overview of the various types of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and ransomware, as well as the technical and non-technical measures that can be used to protect against these threats.
- Risk management: This may include an introduction to risk assessment and management methods, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, and how to use these methods to identify and prioritize risks.
- Security policies and procedures: This may include the development and implementation of security policies and procedures, such as access control policies and incident response plans, as well as how to ensure that these policies and procedures are followed.
- Technical measures: This may include an overview of technical measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and prevention systems, and antivirus software, as well as how to select, configure and maintain these measures.
- Incident response: This may include an introduction to incident response planning and processes, including how to identify and respond to cyber-attacks and other security incidents.
- Legal and ethical issues: This may include an introduction to legal and ethical issues related to cyber security, such as privacy laws and data protection regulations, as well as how to ensure compliance with these laws and regulations.
- Leadership and management: This may include an introduction to leadership and management concepts and practices, and how to apply these concepts to the field of cyber security.
Just one of the subjects that might be addressed in a cybersecurity management course is listed here (Cyber security training). The precise course aims and objectives, as well as the course’s level, will determine the syllabus for that course.
Cyber security management certifications | Certificate in cyber security management
A person’s proficiency in the subject of cyber security can be shown through one of the many different cyber security management certifications that are now offered. These certifications can be helpful for individuals seeking to develop their careers in cyber security since they can show prospective employers that the applicant possesses the abilities and expertise required to be successful in the industry.
The following are a few of the most popularly sought-after certifications in cybersecurity management:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): This is a widely recognized and respected certification in the field of cyber security. It is intended for professionals with at least five years of experience in the field and covers a wide range of topics including security management, risk management, security engineering, and legal and compliance issues.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): This certification is specifically designed for professionals who are responsible for managing and overseeing an organization’s information security program. It covers topics such as security management, risk management, and incident response.
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP): This certification is designed for professionals who are responsible for securing cloud computing environments. It covers topics such as cloud architecture, security design, and compliance.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): This certification is designed for professionals who are responsible for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in an organization’s networks and systems. It covers topics such as penetration testing, network scanning, and ethical hacking techniques.
Best 10 Cyber security management jobs
There are a wide variety of cyber security management jobs available in the field, ranging from entry-level positions to highly specialized roles. Some of the most common types of cyber security management jobs include:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): A CISO is responsible for developing and implementing an organization’s overall cyber security strategy, as well as overseeing the day-to-day management of the organization’s cyber security efforts.
- Information Security Manager: An information security manager is responsible for managing and overseeing an organization’s information security program, including the development and implementation of security policies and procedures, and the selection and maintenance of technical measures such as firewalls and antivirus software.
- Cybersecurity Analyst: A cybersecurity analyst is responsible for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in an organization’s networks and systems, as well as monitoring for and responding to cyber-attacks and other security incidents.
- Penetration Tester: A penetration tester is responsible for testing an organization’s systems and networks to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber attackers.
- Information Security Consultant: An information security consultant is responsible for providing advice and guidance to organizations on how to protect their systems and data from cyber threats.
- Information Security Trainer: An information security trainer is responsible for developing and delivering training programs on cybersecurity topics to organizations and individuals.
- Information Security Auditor: An information security auditor is responsible for reviewing and evaluating an organization’s cyber security practices and policies to ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Information Security Project Manager: An information security project manager is responsible for managing cybersecurity-related projects within an organization, including the development of project plans, budgets, and timelines.
- Information Security Researcher: An information security researcher is responsible for conducting research on cyber security topics and technologies, and sharing their findings with the broader community.
- Information Security Lawyer: An information security lawyer is responsible for advising organizations on legal and compliance issues related to cyber security, such as privacy laws and data protection regulations.
To know more you can visit the website Click here
The cyber security management plan
A cyber security management strategy describes how a company will safeguard its networks, systems, and data from online threats. A collection of policies and procedures that describe how the organization will recognize, evaluate, and reduce threats to its cyber assets, as well as how it will react to and recover from cyberattacks and other security incidents, are often included in such documentation.
A cyber security management strategy should be customized to the unique requirements and threats faced by the organization. It may also incorporate a variety of technical and non-technical safeguards. Among the essential elements of a cyber security management plan could be:
- Risk assessment: This involves identifying and assessing the specific risks that the organization faces, such as the likelihood of a cyber attack and the potential impact of such an attack. This information is used to prioritize and prioritize security efforts.
- Security policies and procedures: This includes the development and implementation of security policies and procedures, such as access control policies, incident response plans, and security awareness training.
- Technical measures: This includes the selection, implementation, and maintenance of technical measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and antivirus software.
- Incident response: This includes the development of plans and processes for responding to and recovering from cyber-attacks and other security incidents.
- Legal and compliance: This includes ensuring that the organization is compliant with relevant laws and regulations related to cyber security, such as privacy laws and data protection regulations.
- Leadership and management: This includes the development of leadership and management practices that support the organization’s cyber security efforts.
To keep it current and useful in defending the organization’s assets and data, a cyber security management strategy should be periodically reviewed and updated.
Cyber security management a Governance Risk and Compliance framework
An organization’s governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) operations are managed using a set of concepts, procedures, and tools called the GRC framework. To make sure that the organization’s cyber security initiatives are in line with its overall risk management and compliance objectives, a GRC framework can be used in the field of cyber security management.
A GRC framework for cyber security management may consist of a number of elements, including:
- Governance: To manage the organization’s cyber security operations, clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes must be established.
- Risk management: Risk management entails determining and evaluating the threats to the organization’s cyber assets, as well as putting countermeasures in place.
- Compliance: This entails making sure that the company’s cyber security initiatives are in line with all applicable laws, rules, and industry standards.
- Monitoring and reporting: This entails keeping track of the organization’s efforts in cyber security and their success, and using that data to guide continuing risk management and compliance initiatives.
Organizations may manage their cyber security risks more successfully and make sure they are in compliance with all applicable rules and regulations by using a GRC framework for cyber security management. It can also offer a disciplined method for managing and enhancing the company’s ongoing cybersecurity initiatives.

MBA in cyber security management | masters in cyber security management | MBA in cyber security management in India | MSc Cyber security management university of law
A graduate-level degree program with a focus on cyber security and business and management principles is the MBA in cyber security management. These courses often include a wide range of subjects relevant to managing and safeguarding an organization’s networks, systems, and data from cyber-attacks. They are created for individuals interested in pursuing leadership roles in the field of cybersecurity.
Courses in an MBA program in cyber security management might cover subjects like:
- Cybersecurity principles and concepts: This may include an overview of the various types of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and ransomware, as well as the technical and non-technical measures that can be used to protect against these threats.
- Risk management: This may include an introduction to risk assessment and management methods, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, and how to use these methods to identify and prioritize risks.
- Security policies and procedures: This may include the development and implementation of security policies and procedures, such as access control policies and incident response plans, as well as how to ensure that these policies and procedures are followed.
- Technical measures: This may include an overview of technical measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and prevention systems, and antivirus software, as well as how to select, configure and maintain these measures.
- Incident response: This may include an introduction to incident response planning and processes, including how to identify and respond to cyber-attacks and other security incidents.
- Legal and ethical issues: This may include an introduction to legal and ethical issues related to cyber security, such as privacy laws and data protection regulations, as well as how to ensure compliance with these laws and regulations.
- Leadership and management: This may include an introduction to leadership and management concepts and practices, and how to apply these concepts to the field of cyber security.
An MBA program in cyber security management may also contain classes on business and management themes like finance, marketing, and strategy in addition to these technical areas. These classes are designed to give students a comprehensive grasp of the commercial and management facets of the cybersecurity industry.
Specialist diploma in Cyber security management
A professional development program that teaches the principles and techniques of managing and safeguarding an organization’s networks, systems, and data from cyber threats is known as a specialist diploma in cyber security management. These courses, which can be taken at the undergraduate or graduate levels, are typically created for professionals who are interested in pursuing jobs in cybersecurity.
A curriculum for a specialized diploma in cyber security management could cover a variety of subjects, including:
- Cybersecurity principles and concepts: This may include an overview of the various types of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and ransomware, as well as the technical and non-technical measures that can be used to protect against these threats.
- Risk management: This may include an introduction to risk assessment and management methods, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, and how to use these methods to identify and prioritize risks.
- Security policies and procedures: This may include the development and implementation of security policies and procedures, such as access control policies and incident response plans, as well as how to ensure that these policies and procedures are followed.
- Technical measures: This may include an overview of technical measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and antivirus software, as well as how to select, configure and maintain these measures.
- Incident response: This may include an introduction to incident response planning and processes, including how to identify and respond to cyber-attacks and other security incidents.
- Legal and ethical issues: This may include an introduction to legal and ethical issues related to cyber security, such as privacy laws and data protection regulations, as well as how to ensure compliance with these laws and regulations.
A master’s or bachelor’s degree program in cyber security may offer a specialist diploma in cyber security management as a stand-alone program or as a component of a larger degree program. A specialty diploma program’s exact course requirements and syllabus will rely on the programs.
American cyber security management
The ideas and procedures for managing and safeguarding a company’s networks, systems, and data from online attacks are referred to as American cyber security management. This may involve choosing and configuring technological measures like firewalls and antivirus software, managing incident response operations, and developing and implementing security policies and procedures.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a government organization in the United States that creates standards and regulations for cybersecurity management. A well-liked structure that instructs businesses on how to control their cyber security threats is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
There are numerous more organizations and resources, in addition to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, that offers direction and assistance for American cybersecurity management. These consist of both private sector businesses that offer cyber security consulting and training services as well as professional organizations like the International Association of Computer Science and Information Technology (IACSIT) and the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
To defend an organization’s networks, systems, and data from cyber threats, American cyber security management often entails a combination of technological measures and non-technical measures, such as policies and procedures.
Supply chain cyber security management
The ideas and procedures for defending a company’s supply chain against cyber threats are referred to as supply chain cyber security management. The network of companies, groups, and people who work together to produce, distribute, and deliver goods and services is referred to as the supply chain. This can include vendors, producers, distributors, logisticians, and other associates.
Supply chain cyber security management is determining and evaluating the risks that a company’s supply chain may face with respect to cyber-attacks and putting protective measures in place. This may involve choosing and configuring technological measures like firewalls and antivirus software, managing incident response operations, and developing and implementing security policies and procedures.
Supply chain cyber security management is fraught with difficulties. It may be difficult to identify and manage risk for a business, for instance, if it has little visibility into the cyber security procedures used by its suppliers. Additionally, it can be challenging to organize and put into place efficient cyber security measures across all of the many partners and stakeholders due to the complex and frequently global nature of supply chains.
In general, supply chain cyber security management is a crucial component of an organization’s overall cyber security activities because it ensures that the organization’s networks, systems, and data are safe against cyber threats that could come through the supply chain.
Cyber and information security management
The management of an organization’s networks, systems, and data (for data security) as well as the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its information are all covered by the principles and procedures of cyber and information security. This entails determining and evaluating the risks that the company confronts in relation to cyber threats, as well as putting policies in place to lessen those risks.
The development and implementation of security policies and procedures, the choice and configuration of technical measures like firewalls and antivirus software, and the management of incident response initiatives are just a few examples of the technical and non-technical measures that may be included in cyber and information security management.
Additionally, it might entail the deployment of safeguards like data encryption and access control policies to ensure the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of the organization’s information.
Technical know-how along with managerial and leadership abilities are necessary for effective cyber and information security management. It also calls for the capacity to adjust to evolving risks and technological advancements, as well as a proactive approach to risk management.
Cyber risk security management
The process of detecting, evaluating, and managing the risks that an organization confronts in regard to cyber threats is known as cyber risk management. This entails identifying the digital assets that the company needs to safeguard, such as its networks, systems, and data, as well as estimating the likelihood and potential consequences of certain cyber threats. The organization can put steps in place to mitigate the risks identified as a result of this assessment.
The development and implementation of security policies and procedures, the choice and configuration of technical measures like firewalls or WAF and antivirus software, and the management of incident response efforts are just a few examples of the various technical and non-technical actions that can be included in cyber risk management. Implementing safeguards like data encryption (for data security) and access control regulations, which protect the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of the organization’s information may also be necessary.
A proactive approach to risk identification and assessment, as well as the capacity to adjust to evolving threats and technology, are necessary for effective cyber risk management. Ensure that the organization’s cyber risk management initiatives are well-coordinated and successful, it also demands strong leadership and management abilities.

