Businesses employ DR (Disaster Recovery) and BCP (Business Continuity Planning) as crucial techniques to foresee interruptions and catastrophes and to respond to them. The process of recovering from a disaster or significant interruption is referred to as disaster recovery (DR). This can range from a cyberattack or power loss to a natural disaster like a storm or earthquake. DR entails the creation of a plan, as well as the tools and resources required to execute that plan, to restore crucial systems and procedures in the case of a disaster.
In addition to Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity Planning (BCP) is a more general term that refers to the planning and preparation required to ensure that an organization can continue to run and provide critical goods and services both during and after a disruption or disaster. This may entail locating and reducing potential hazards, creating backup plans, testing them, and instructing staff members on how to use them.
Both DR and BCP are crucial for assuring an organization’s resilience and stability and can lessen the effects of disruptions on business operations, clients, and staff.
BCP vs DR | Business Continuity vs Disaster Recovery | What’s The Difference Between DR And BCP? | Key Differences Between BCPs and DR Plans | Difference between DR & BCP
Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) are related but separate ideas that assist firms in preparing for and handling emergencies and disruptions.
The phrase “Business Continuity Planning” (BCP) refers to a broader concept that refers to the planning and preparation required to guarantee that a company can continue to function and provide vital goods and services both during and after an interruption or disaster. This can involve locating and minimizing potential hazards, creating backup plans, testing them, and instructing staff members on how to use them. BCP seeks to lessen the effects of interruptions on business operations, clients, and staff while also focusing on an organization’s general resilience and stability.
Recovery from a disaster or significant interruption is referred to as disaster recovery (DR). This can range from a cyberattack or power loss to a natural disaster like a storm or earthquake. DR entails the creation of a plan, as well as the tools and resources required to execute that plan, to restore crucial systems and procedures in the case of a disaster. DR is usually a part of a wider BCP plan and is concentrated on the technical aspects of recovering after a disaster, such as restoring data and systems.
In conclusion, DR is focused on the technical aspects of recovering from a disaster and restoring vital systems and processes, whereas BCP is a broader term that involves the planning and preparation required to ensure that an organization can continue to operate during and after a disruption or disaster.
BCP DR plan template | Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery Planning (BCP & DRP)
Organizations can utilize both a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and a Disaster Recovery Plan (DR) to plan for and respond to disruptions and catastrophes. These plans lay out the actions that a company will take to keep running and provide necessary goods and services both during and after a disaster or significant interruption.
A BCP/DR plan template may want to include the following significant components:
- Introduction: This section should give a general description of the goals and parameters of the strategy, as well as any pertinent background data.
- Threats and vulnerabilities: This section should list and evaluate any potential threats or weaknesses the organization may be exposed to, such as power outages, cyberattacks, and natural catastrophes.
- Planning for contingencies: This section should describe the steps the company will take to lessen the effects of disruptions, such as creating backup systems, finding alternative workspaces, or putting communication channels in place.
- Recovery planning: This section should describe the measures the company will take to restore crucial systems and operations in the event of a disaster, including protocols for data backup and restoration, system recovery, and communication with staff members and stakeholders.
- Testing and upkeep: This section should outline how the business will test and keep the BCP/DR plan up to date, including personnel training, routine drills, and document updates.
- Resources: The people, tools, and money that will be required to carry out the BCP/DR plan should all be listed in this section.
The processes for communication and coordination with staff members, clients, vendors, and other stakeholders during disruption should be described in this area.
The particular components of a BCP/DR plan will vary depending on the needs and hazards of the organization because every organization is unique. The overall outline provided by this template may need to be modified to fit the unique requirements of your company.
BCP DR certification | DR BCP certification
The goal of the Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Disaster Recovery (DR) certification programs is to give professionals the information and abilities they need to create and implement successful BCP and DR strategies for organizations. Professional associations, academic institutions, or for-profit training organizations can all offer these programs.
BCP and DR certifications often call for passing an exam in addition to completing training or coursework. Depending on the program, different requirements may apply for certification, but they could include:
- Coursework or training in BCP and DR concepts, principles, and best practices
- Experience in developing and implementing BCP and DR plans
- A demonstrated understanding of the unique needs and risks of different types of organizations
Some examples of BCP and DR certification programs include:
- Certified Business Continuity Professional (CBCP) offered by the Disaster Recovery Institute International (DRI)
- Certified Continuity Manager (CCM) offered by the Business Continuity Institute (BCI)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) offered by (ISC)², which includes a focus on disaster recovery and business continuity
- Obtaining BCP and DR certification can help professionals demonstrate their expertise and knowledge in these areas, and may be beneficial for those seeking career advancement or job opportunities in fields related to BCP and DR.
BCP in banking | DR in Banking & Fintech
Banks and other financial organizations employ Business Continuity Planning (BCP) as a crucial technique to get ready for disruptions and emergencies and to handle them. BCP entails the creation of strategies and procedures to guarantee that the organization can carry on and provide vital goods and services both during and after a disaster or significant disruption.
Due to the crucial role that financial institutions play in the economy, BCP is particularly significant in the banking sector. Disruptions or emergencies that impair a bank’s ability to function could have major repercussions for the bank’s clients, staff, and overall economy.
When creating a BCP plan, banks may need to take certain factors into mind, such as:
- Maintaining access to critical systems and data: To run their businesses, banks depend on a variety of systems and data, including core banking systems, client information, and financial records. Measures to guarantee that these systems and data are safe and can be swiftly restored in the case of a disaster should be included in BCP plans.
- Ensuring the availability of cash: Providing customers with access to cash is the responsibility of banks, and supply chain or transportation system interruptions can make this challenging. Measures to guarantee banks have access to enough cash reserves to meet client needs during disruption should be included in BCP plans.
- Maintaining communication with customers and stakeholders: Because disruptions can lead to customer uncertainty and worry, it’s critical for banks to keep in touch with their clients during these moments. BCP plans must have procedures for contacting clients and other stakeholders in the event of an interruption.
In the banking sector, a BCP plan’s overall objective is to make sure that the bank can continue providing services to its clients and carrying out its commitments even in the event of emergencies or disruptions.
DR BCP best practices
Organizations can employ critical tactics like Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) to get ready for and handle emergencies and disruptions. There are a few best practices that firms should adhere to in order to make sure that these strategies are successful:
- Identify and assess risks: It’s critical to recognize and evaluate the organization’s vulnerabilities and potential hazards, such as those posed by natural disasters, cyberattacks, power outages, and other disruptions. This will assist the organization in selecting the appropriate contingency and recovery plans.
- Develop a comprehensive plan: A BCP/DR strategy should be thorough and include every facet of the business, including crucial procedures and systems, communication standards, and personnel duties.
- Test and maintain the plan: It is essential to regularly test and maintain the BCP/DR strategy to make sure it is current and effective. This can entail carrying out drills and exercises, updating the plan’s documentation, and instructing staff members on how to carry it out.
- Involve all stakeholders: It’s crucial to include all parties in the creation and execution of the BCP/DR strategy, including staff members, clients, suppliers, and other partners. This will guarantee that everyone is aware of their obligations and roles and is ready to take action in the case of a disruption.
- Communicate and coordinate: During a disruption, good and clear communication is crucial. Protocols for coordination with other organizations and agencies as well as communication with staff, clients, and other stakeholders should be part of the BCP/DR plan.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can improve the efficiency of their BCP/DR plans and more effectively plan for and handle emergencies and interruptions.
DR BCP summary – salesforce services
Organizations can employ Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Disaster Recovery (DR) as effective tools to plan for and handle emergencies and disruptions. These strategies entail the creation of plans and procedures to guarantee that the business can carry on and deliver crucial goods and services both during and after a disaster or significant disruption.
Salesforce is a cloud-based platform for customer relationship management (CRM) that offers a variety of tools and services to assist businesses in managing their client connections and corporate operations. For customers to preserve their data and ensure business continuity in the case of an interruption, Salesforce offers a number of BCP and DR services.
The following are some instances of Salesforce BCP and DR services:
Data backup and recovery:
Salesforce provides a range of tools and services to help customers protect and recover their data, including automated backups, point-in-time recovery, and data export.
Disaster recovery site:
Salesforce offers a disaster recovery site that can be used as a backup location in the event of a disaster. This site is fully replicated and can be used to restore critical systems and processes.
Emergency notification system:
Salesforce has an emergency notification system that can be used to alert employees and stakeholders in the event of a disruption. This system allows customers to send targeted messages to specific groups of people, such as employees in a particular location or customers with specific needs.
Service level agreements (SLAs):
Salesforce provides service level agreements (SLAs) that outline the level of service that customers can expect during and after a disruption. These SLAs may include commitments on uptime, data recovery, and other critical service components.
Overall, Salesforce provides a range of BCP and DR services to help customers protect their data and maintain business continuity in the event of a disruption.
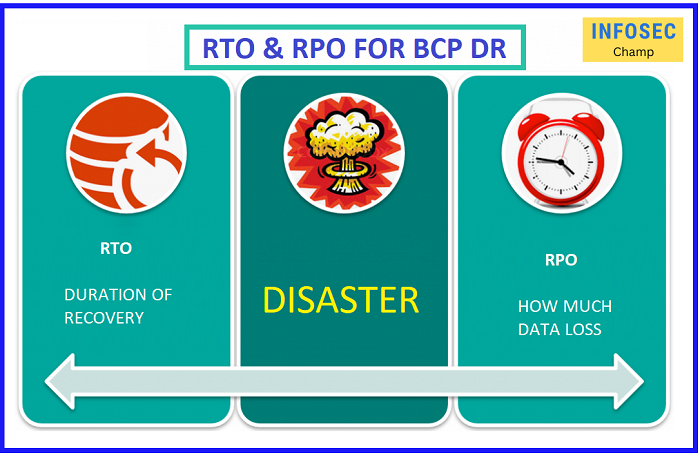
DR BCP with rto rpo
Organizations employ business continuity planning (BCP) and disaster recovery (DR) as key tools to anticipate and handle disruptions and emergencies. These strategies entail the creation of plans and procedures to guarantee that the business can carry on and deliver crucial goods and services both during and after a disaster or significant disruption.
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) are key metrics that are used to measure the effectiveness of DR and BCP plans. These metrics can help organizations determine the level of resilience and stability that is required to meet their business needs and objectives.
Here is a brief explanation of these terms:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the amount of time that it is expected to take to recover critical systems and processes after a disaster or major interruption. RTO is often expressed as a specific time frame, such as 4 hours, 12 hours, or 24 hours.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the point in time to which data and systems must be restored after a disaster or major interruption. RPO is often expressed as a specific time frame, such as 1 hour, 4 hours, or 12 hours.
Both RTO and RPO are important considerations when developing DR and BCP plans, as they help organizations determine the level of resilience and stability that is required to meet their business needs and objectives. It is important to balance the costs and benefits of different RTO and RPO levels, as higher levels of resilience and stability may come with higher costs and complexity.
Physical security in DR/BCP scenarios | What is DR BCP and contingency planning?
In disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity planning (BCP) scenarios, physical security is a crucial factor. Physical security refers to the precautions that businesses take to safeguard their assets, personnel, and facilities from potential physical threats and weaknesses.
Physical security measures in DR and BCP situations can help secure the safety and security of workers and stakeholders as well as safeguard vital infrastructure and systems from harm or disturbance. The following are some instances of physical security measures that may be pertinent in DR and BCP scenarios:
- Access control: Access control measures, such as security guards, locked doors, and security cameras, can help prevent unauthorized access to facilities and critical infrastructure.
- Environmental controls: Environmental controls, such as temperature and humidity control, can help protect equipment and critical systems from environmental damage.
- Physical barriers: Physical barriers, such as fencing or walls, can help prevent unauthorized access to facilities and critical infrastructure.
- Security protocols: Security protocols, such as visitor screening and employee identification, can help prevent unauthorized access to facilities and critical infrastructure.
It is important to consider physical security as part of a broader DR and BCP strategy and to ensure that physical security measures are integrated with other contingency and recovery measures. This can help organizations ensure the safety and security of their employees and stakeholders, as well as protect critical systems and infrastructure from damage or disruption.
Datacenter (dc) DR BCP
DC (Data Center) DR (Disaster Recovery) and BCP (Business Continuity Planning) are important strategies that organizations use to prepare for and respond to disruptions and emergencies. These strategies involve the development of plans and procedures to ensure that the organization can continue to operate and deliver essential products and services during and after a disaster or major interruption.
A data center is a place where vital computer infrastructure, such as servers, storage systems, and networking tools, are housed. Because they offer the computational power and storage required to support corporate processes and applications, data centers are essential to the operation of many enterprises.
The planning and preparation necessary to make sure that data centers can continue to run and provide important services during and after a disruption or disaster are the focus of DC DR and BCP. This may entail locating and reducing potential hazards, creating backup plans, testing them, and instructing staff members on how to use them.
When creating DC DR and BCP strategies, companies may need to take certain factors into mind. These factors include:
Access to vital systems and data must be maintained since data centers depend on a variety of systems and data to support corporate operations and applications. It’s crucial to make sure that these systems and data are safeguarded and can be swiftly restored in case of an emergency.
Assuring the availability of power and cooling: To support the functioning of vital systems and infrastructure, data centers need a dependable supply of power and cooling. Measures to guarantee that these systems are secured and can be promptly restored in the case of an interruption should be included in BCP and DR strategies.
Maintaining communication with employees and stakeholders: During disruptions, employees and stakeholders may get confused or worried, thus it is crucial for enterprises to maintain efficient contact with them. Protocols for contacting staff members and other stakeholders during disruption should be included in BCP and DR plans.
In general, the purpose of DC DR and BCP is to make sure that data centers can continue to run and provide vital services both during and after an interruption or disaster.
At what periodicity DR/BCP test runs are to be conducted
Depending on the particular requirements and dangers of a company, the frequency of Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) test runs will vary. To ensure that DR and BCP plans are current and functional, businesses are generally advised to test and maintain them on a regular basis. This is verified as part of the DR/BCP strategy to protect data security as well.
The following are a few variables that may affect how often DR and BCP test runs are conducted:
- The complexity and scope of the DR and BCP plan: To make sure that all systems and processes are adequately tested and maintained, organizations with more intricate or extensive DR and BCP plans may need to do test runs more frequently.
- The level of risk and potential impact of disruptions: To make sure that their DR and BCP plans are strong and effective, organizations that are more exposed to risk or that would be more severely affected by disruptions may need to test them more frequently.
- Changes to the organization or its operating environment: Updates to the DR and BCP plans may be necessary due to changes in the organization or its operating environments, such as the introduction of new technologies or regulatory requirements. To keep the designs current and efficient, regular test runs can be helpful.
When it comes to the frequency of DR and BCP test runs, there is no one size fits all solution. Organizations must take into account their unique requirements and risks in order to create a testing plan that is suitable for their situation.

AWS DR BCP
AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers a variety of tools and services to assist businesses in creating and putting into action their Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) plans. AWS is a cloud-based platform that provides a variety of services, such as computing, storage, networking, and database services, which may be used to create, deploy, and manage infrastructure and applications.
The following are some instances of AWS products and services that can be utilized for DR and BCP:
AWS Backup:
AWS Backup is a fully managed backup service that makes it easy to automate the process of backing up data and systems. AWS Backup integrates with other AWS services, such as Amazon S3 and Amazon EFS, to provide a centralized solution for backing up data and systems.
AWS Disaster Recovery:
AWS Disaster Recovery is a service that helps organizations design, implement, and test DR plans. AWS Disaster Recovery includes a range of tools and resources, including best practices guides and architecture patterns, to help organizations develop effective DR strategies.
AWS Site-to-Site VPN:
AWS Site-to-Site VPN is a service that allows organizations to establish a secure connection between their on-premises infrastructure and their AWS resources. This can be used to create a DR solution that enables organizations to fail over to their AWS resources in the event of a disaster.
AWS CloudFormation:
Businesses may automate the development and maintenance of their AWS resources with the help of AWS CloudFormation. The infrastructure and configuration of an organization’s AWS resources can be defined in templates created with CloudFormation, making it simpler to deploy and manage such resources.
AWS offers a variety of tools and services that can be used to create and put into practise successful DR and BCP strategies.
Azure DR BCP
Microsoft Azure is a cloud-based platform that provides a range of tools and services to help organizations develop and implement Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) strategies. Azure offers a wide range of services, including computing, storage, networking, and database services, that can be used to build, deploy, and operate applications and infrastructure.
Some examples of Azure tools and services that can be used for DR and BCP include:
Azure Backup:
Azure Backup is a fully managed backup service that makes it easy to automate the process of backing up data and systems. Azure Backup integrates with other Azure services, such as Azure Storage and Azure Files, to provide a centralized solution for backing up data and systems.
Azure Site Recovery:
Azure Site Recovery is a service that helps organizations design, implement, and test DR plans. Azure Site Recovery includes a range of tools and resources, including best practices guides and architecture patterns, to help organizations develop effective DR strategies.
Azure Virtual Network:
Azure Virtual Network is a service that allows organizations to create a virtual network in Azure and connect it to their on-premises infrastructure using a VPN connection. This can be used to create a DR solution that enables organizations to failover to their Azure resources in the event of a disaster.
Azure Resource Manager:
Azure Resource Manager is a service that allows organizations to automate the creation and management of their Azure resources. Resource Manager can be used to create templates that define the infrastructure and configuration of an organization’s Azure resources, making it easier to deploy and manage those resources.
Overall, Azure provides a range of tools and services that can be used to develop and implement effective DR and BCP strategies.
Dropped kerb BCP council
A portion of pavement or a sidewalk that has been reduced to the same level as the road is referred to as a “dropping kerb,” also known as a “curb cut.” To allow vehicles to enter driveways or other private properties from the road, dropped kerbs are frequently constructed at those entrances.
A council (often referred to as a local government or municipality) may need to take dropped kerbs into consideration as part of their planning and preparation for interruptions or emergencies in the context of Business Continuity Planning (BCP). For instance, a council might have to make sure dropped kerbs are kept up and in excellent shape to provide access to private property for emergency vehicles and other vital services as needed.
In general, when creating and implementing BCP plans, councils should take into account the demands of all stakeholders, including citizens, companies, and emergency services. This could entail working with other agencies and groups, creating and distributing concise plans and practices for handling interruptions and emergencies, and cooperating with them.
FAQ:
1. What are DR and BCP?
It is planning related to Disaster recovery and Business continuity planning (BCP) for business safety and support continuity of the business in case of unwanted event occur or disasters occur like tsunamis, earthquakes etc.
2. Is DR a part of BCP?
Yes, Disaster Recovery (DR) is a component of Business Continuity Planning (BCP). BCP is a broader strategy that involves the development of plans and procedures to ensure that an organization can continue to operate and deliver essential products and services during and after a disaster or major interruption. DR is a specific aspect of BCP that focuses on the recovery of critical systems and processes after a disaster or major interruption.
3. What is fullform of BCP DR?
Business Continuity Planning (BCP) is the process of developing plans and procedures to ensure that an organization can continue to operate and deliver essential products and services during and after a disaster or major interruption.
Disaster Recovery (DR) is a specific aspect of BCP that focuses on the recovery of critical systems and processes after a disaster or major interruption.
4. What does BCP mean?
As per the above definition and full form.
5. What is DR in TCS?
TCS (Tata Consultancy Services) is a global IT services and consulting company that provides a range of services to clients in various industries. It is likely that the term “DR” in the context of TCS refers to Disaster Recovery, which is a strategy that organizations use to prepare for and respond to disruptions and emergencies.
6. How do you perform a DR test?
An organization’s disaster recovery plans and procedures are tested to see how well they work by simulating a disaster or significant interruption. A company should conduct DR testing to make sure that its plans and procedures are up to par and that it is ready to respond to crises and disruptions.


